Jun 2, 2022 Nutrition Guidance for Military & First-Responders
In addition to exercise, proper nutrition plays a major role in maintaining total fitness. Good dietary habits greatly enhance your ability to perform at your maximum potential. Eating a variety of foods and maintaining adequate energy balance are basic guidelines for a healthy diet.
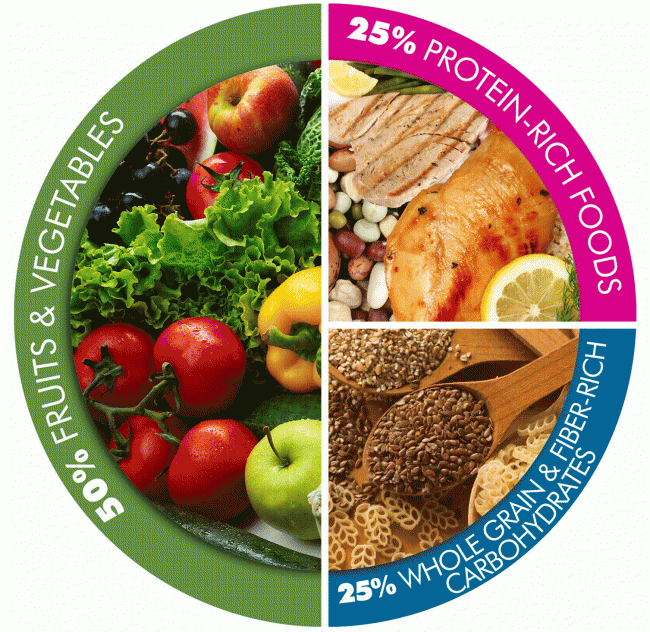
Below is a sample nutrition guide for military soldiers and first responders based on information provided by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and ChooseMyPlate.gov.
What To Eat
- 55-65% from Carbohydrates to fuel muscles and brain
- Eat whole grain and whole wheat bread (1st ingredient needs to be “whole grain flour” or “whole wheat flour”), whole grain cereals, brown rice, whole-wheat pasta, fruits vegetables, beans and legumes, and low-fat dairy products.
- 20-30% from Fat to absorb vitamins and cushion organs, tissues, and joints
- Eat healthy, unsaturated fats (EVOO, olives, nuts and seeds, natural peanut butter, avocado, fatty fish, and flax seeds).
- Limit saturated fats (fried, animal fats, hydrogenated, and processed foods).
- Avoid trans fats (hydrogenated and processed foods).
- At least 75 grams of total fat per day
- 15-20% from Protein to build and repair muscle
- Eat lean meats (poultry, fish, lean sirloin, and pork tenderloin), eggs, low-fat dairy products, nuts and seeds, beans, and legumes.
- The best diet contains adequate but not excessive protein. Extra protein does not build extra muscle — exercise does.
- Protein needs per pound of bodyweight
- Tactical Athlete — 0.5-.80 gm pro/lb.
- Tactical Athlete Building Muscle Mass — 0.7-1.0 gm pro/lb.
- Tactical Athlete Restricting Calories (needs weight loss) — 0.8-1.0 gm pro/lb.
When To Eat
- A key to healthy eating is fueling your body throughout the day, eating every 3-4 hours is ideal.
- BEFORE EXERCISE
- Eat a carbohydrate-rich meal with protein 3-4 hours prior to exercise.
- Examples: Banana and peanut butter sandwich and milk; Bagel sandwich with lean meat, cheese, and veggies; Chicken, rice, and veggies; Spaghetti with lean meat and a salad.
- Eat a carbohydrate-rich snack 30 minutes to 2 hours before training/competition.
- The timing is wide to account for the difference between each individual — some can eat prior without getting an upset stomach and others cannot.
- Examples: A piece of fruit; A bagel; Or a granola bar
- Eat a carbohydrate-rich meal with protein 3-4 hours prior to exercise.
- AFTER EXERCISE
- Eat a combination of carbs and protein within 30 minutes of exercise.
- Examples: 8-16 oz. chocolate milk; Turkey sandwich; Flavored Greek yogurt and fresh fruit; Fruit and yogurt smoothie
- Eat a balanced meal containing all the food groups (protein/dairy, grains, fruit, veggies) within 2 hours.
- Examples: Homemade burrito (tortilla, beans, lettuce, tomato, low-fat cheese, and salsa); Grilled chicken, brown rice, veggies, and fruit; Tuna salad made with veggies, whole grain crackers, provolone cheese, and fruit.
- Eat a combination of carbs and protein within 30 minutes of exercise.
*For Maximum Physical & Mental Performance, at every meal, eat carbohydrates, protein, and drink milk
TROUBLESHOOTING NUTRITION TIPS
| PROBLEM | WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? | FOOD SOURCES | RESULT |
| LOW ENERGY; SLUGGISH; EASILY TIRED | EAT FOODS RICH IN CARBOHYDRATES | WHOLE WHEAT BREAD, CEREAL, PASTA, RICE, PEAS, CORN, POTATOES, FRUITS, VEGGIES | CARBOHYDRATES PROVIDE FUEL FOR MUSCLES AND BRAIN |
| MUSCLE STRAINS; INJURIES; SLOW TO RECOVER | EAT GOOD FOOD SOURCES OF PROTEIN | CHICKEN, FISH, BEEF, CHEESE, MILK, NUTS, SEEDS, PEANUT BUTTER | FASTER RECOVERY FROM INJURY; REPAIR MUSCLES |
| TROUBLE SUSTAINING ENERGY OUTPUT | EAT HEALTHY FAT SOURCES | NUTS, SEEDS, PEANUT BUTTER, EVOO, OLIVES, FISH, AVOCADO | GREATER ENERGY OUTPUT; BUILD MUSCLE MORE EFFICIENTLY |
| CONSTIPATION | INCREASE FIBER IN DIET | WHOLE GRAIN BREAD & CEREAL; BEANS, PEAS, FRUITS, AND VEGETABLES | RELIEF! |
| DIFFICULTY MAINTAINING BODY TEMP; LOW ENERGY | INCREASE IRON-RICH FOOD SOURCES | BEEF, CHICKEN, TURKEY, FISH, SPINACH, KALE, BEANS, PEAS, FORTIFIED BREADS, CEREALS, AND JUICE | GREATER ENERGY; BETTER TOLERANCE TO COLD |
| BROKEN BONES; STRESS FRACTURES; BRITTLE TEETH | INCREASE CALCIUM-RICH FOODS. INCREASE VITAMIN D FOOD SOURCES | MILK, YOGURT, CHEESE, SALMON, BROCCOLI, KALE, CALCIUM FORTIFIED FOODS, VITAMIN D FORTIFIED MILK, EGGS, SEAFOOD, FORTIFIED CEREALS | STRENGTHEN BONES AND TEETH; VITAMIN D HELPS ABSORB CALCIUM AND THUS HELPS PREVENT FRACTURES AND BONE WEAKNESS |
| INCREASE MUSCLE MASS | INCREASE CALORIES AND PROTEIN RICH FOODS | FISH, CHICKEN, LEAN BEEF, PORK, MILK, EGGS, CHEESE YOGURT, PEANUTS, NUTS/SEEDS, BEANS, AND LENTILS | PROTEIN INTAKE MUST BE COMBINED WITH WEIGHT TRAINING TO BUILD MUSCLE MASS |
Hydration
- Your bodyweight in pounds divided by 2 = the minimum number of ounces of fluids you need per day. (This does not include the amount of exercise you do or the climate you are in.*) Example: 180 pounds/2=90 ounces of water per day
» ALSO SEE: Combatting Stress with Nutrition Post-Workout Recovery
Half Gallon = 64 Ounces | 1 Gallon = 128 Ounces | 1 Canteen = 32 ounces
With Exercise Add:
- 16 Ounces – 2 hours prior to exercise
- 4-8 Ounces – 10 minutes prior to exercise
- 4-8 Ounces – every 20 minutes during exercise
- 16-24 Ounces – after exercise
For Exercise Lasting Longer than 60 Minutes:
- Use sports drinks for hydration, glucose, and electrolytes to improve endurance performance
- Per 8 ounces: 12-24 grams of Carbohydrate; 110-170 mg of Sodium; 20-50 mg of Potassium
| SYMPTOMS OF DEHYDRATION | FOR THESE SYMPTOMS, NOTIFY INSTRUCTOR IMMEDIATELY |
| THIRSTYHEADACHEDRY MOUTHDRY SKINFATIGUEDIZZINESS | CHILLSINCREASED HEART RATEMUSCLE CRAMPSNAUSEA/VOMITINGSWOLLEN STOMACHCONFUSION |
*Nutrition Information provided by U.S. Department of Agriculture and ChooseMyPlate.gov.



